| Index | Red | Green | Blue |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | |||
| 1 | |||
| 2 | |||
| 3 | |||
| . | |||
| . | |||
| 255 |
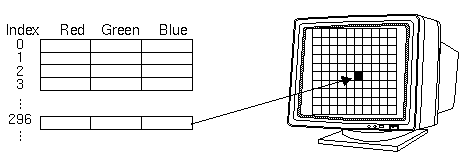
- Porting old color-index mode applications
- HW/SW constraints on the number of bitplanes
- Color-map animation
| Index | Red | Green | Blue |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | |||
| 1 | |||
| 2 | |||
| 3 | |||
| . | |||
| . | |||
| 255 |

void glIndex{ sifd ub} ( TYPE c );
void glIndex{ sifd ub}v ( const TYPE *c );
void glClearIndex ( GLfloat cindex );
Setup color map (related to Window system):
void glutSetColor( int cell, GLfloat red, GLfloat green, GLfloat blue );
|
For example, build a 32 continous color indices with slightly differing shades of 'yellow'.
for ( i = 0; i < 32; i++ ) {
glutSetColor ( 16+i, 1.0*(i/32.0), 1.0*(i/32.0), 0.0);
}
|

while (1) {
get_viewing_point_from_mouse_position();
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT);
draw_3d_object_A();
draw_3d_object_B();
}
|
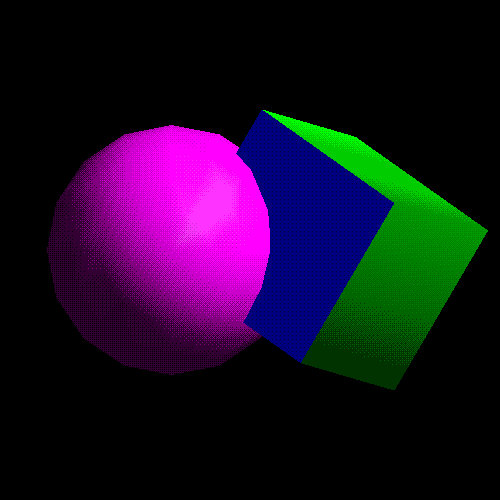
glutInitDisplayMode ( GLUT_DEPTH | ... );
glEnable ( GL_DEPTH_TEST );
...
while(1) {
glClear( GLCOLOR_BUFFER_BIT | GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT );
get_viewing_point_from_mouse_position();
draw_3d_object_A();
draw_3d_object_B();
}
|


#include |
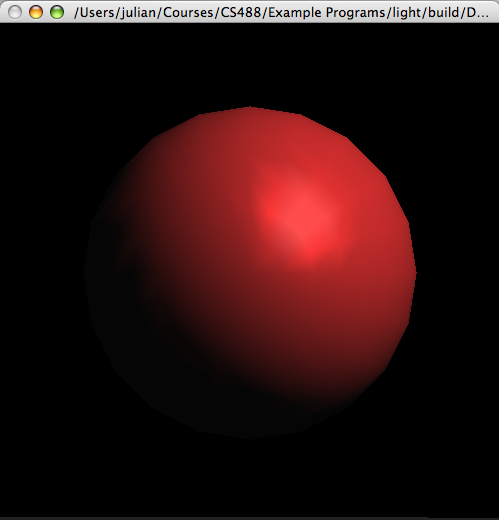 |
|
void glLight{if}(GLenum light, GLenum pname, TYPE param);
void glLight{if}v(GLenum light, GLenum pname, TYPE *param); |
|
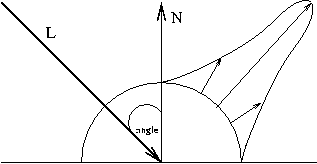
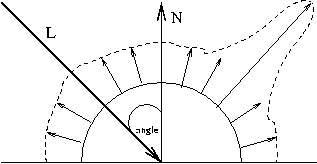
Creates the light specified by light, which can be GL_LIGHT0, GL_LIGHT1, ... , or GL_LIGHT7. The characteristic of the light being set is defined by pname, which specifies a named parameter (see Table below). param indicates the values to which the pname characteristic is set; it's a pointer to a group of values if the vector version is used, or the value itself if the nonvector version is used. The nonvector version can be used to set only single-valued light characteristics. |
| Parameter Name | Default Value | Meaning | |
|---|---|---|---|
| GL_AMBIENT | (0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0) | ambient RGBA intensity of light | |
| GL_DIFFUSE | (1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0) | diffuse RGBA intensity of light | |
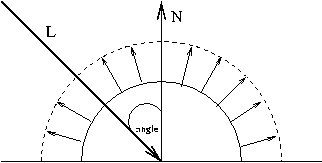
| GL_SPECULAR | (1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0) | specular RGBA intensity of light | GL_POSITION | (0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0) | (x, y, z, w) position of light |
| GL_SPOT_DIRECTION | (0.0, 0.0, -1.0) | (x, y, z) direction of spotlight | |
| GL_SPOT_EXPONENT | 0.0 |
spotlight exponent
(how concentrated is the light) |
|
| GL_SPOT_CUTOFF | 180.0 | spotlight cutoff angle | |
| GL_CONSTANT_ATTENUATION ("falloff" function) | 1.0 | constant attenuation factor | |
| GL_LINEAR_ATTENUATION ("falloff" function) | 0.0 | linear attenuation factor ("falloff" function) | GL_QUADRATIC_ATTENUATION | 0.0 | quadratic attenuation factor |
Attenuation (define how the intensities of light decay)
| attenuation factor = | 1 kc + kld + kqd2 |
d = distance between the light's position and the vertex kc = GL_CONSTANT_ATTENUATION kl = GL_LINEAR_ATTENUATION kq = GL_QUADRATIC_ATTENUATION
By default, kc = 1.0, kl = kq = 0.0.
You can give these parameters different values:
glLightf(GL_LIGHT0, GL_CONSTANT_ATTENUATION, 2.0); glLightf(GL_LIGHT0, GL_LINEAR_ATTENUATION, 1.0); glLightf(GL_LIGHT0, GL_QUADRATIC_ATTENUATION, 0.5); |
Spotlights ( default GL_SPOT_CUTOFF=180 )
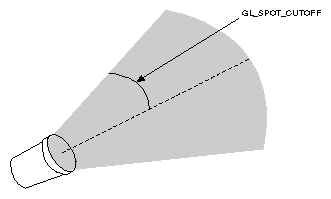
|
glLightf(GL_LIGHT0, GL_SPOT_CUTOFF, 45.0);
GLfloat spot_direction[] = { -1.0, -1.0, 0.0 }; glLightfv(GL_LIGHT0, GL_SPOT_DIRECTION, spot_direction); |
Multiple lights
Can have up to 8 light sources.
Example: Second light source
GLfloat light1_ambient[] = { 0.2, 0.2, 0.2, 1.0 };
GLfloat light1_diffuse[] = { 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0 };
GLfloat light1_specular[] = { 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0 };
GLfloat light1_position[] = { -2.0, 2.0, 1.0, 1.0 };
GLfloat spot_direction[] = { -1.0, -1.0, 0.0 };
glLightfv(GL_LIGHT1, GL_AMBIENT, light1_ambient);
glLightfv(GL_LIGHT1, GL_DIFFUSE, light1_diffuse);
glLightfv(GL_LIGHT1, GL_SPECULAR, light1_specular);
glLightfv(GL_LIGHT1, GL_POSITION, light1_position);
glLightf(GL_LIGHT1, GL_CONSTANT_ATTENUATION, 1.5);
glLightf(GL_LIGHT1, GL_LINEAR_ATTENUATION, 0.5);
glLightf(GL_LIGHT1, GL_QUADRATIC_ATTENUATION, 0.2);
glLightf(GL_LIGHT1, GL_SPOT_CUTOFF, 45.0);
glLightfv(GL_LIGHT1, GL_SPOT_DIRECTION, spot_direction);
glLightf(GL_LIGHT1, GL_SPOT_EXPONENT, 2.0);
glEnable(GL_LIGHT1);
|
Position
The fourth component of light_position is 0.0 which signifies
the light is directional light.
By default, GL_POSITION is (0, 0, 1, 0), which defines a
directional light. And (x, y, z) is its direction.
|
GLfloat light_position[] = { 5.0, 10.0, 2.0, 1.0 };
glLightfv(GL_LIGHT0, GL_POSITION, light_position); |
The location is transformed by the model view
matrix and stored in the eye coordinate system
(i.e. relative to the eye )
Note that by default (i.e. gluLookAt() is not called ), the
camera ( eye ) is situated at the origin, pointing down the
negative z-axis.
By default, a positional light radiates in all directions.
glViewport (0, 0, (GLsizei) w, (GLsizei) h);
glMatrixMode (GL_PROJECTION);
glLoadIdentity();
if (w <= h)
glOrtho (-1.5, 1.5, -1.5*h/w, 1.5*h/w, -10.0, 10.0);
else
glOrtho (-1.5*w/h, 1.5*w/h, -1.5, 1.5, -10.0, 10.0);
glMatrixMode (GL_MODELVIEW);
glLoadIdentity();
/* later in init() */
GLfloat light_position[] = { 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0 };
glLightfv(GL_LIGHT0, GL_POSITION, position);
|
To rotate or translate the light position: light moves relative to a stationary object.
static GLdouble spin;
void display(void)
{
GLfloat light_position[] = { 0.0, 0.0, 1.5, 1.0 };
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT | GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT);
glPushMatrix();
gluLookAt (0.0, 0.0, 5.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0, 0.0);
glPushMatrix();
glRotated(spin, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0);
glLightfv(GL_LIGHT0, GL_POSITION, light_position);
glPopMatrix();
glutSolidTorus (0.275, 0.85, 8, 15);
glPopMatrix();
glFlush();
}
|
Example 6-6. Moving a Light with Modeling Transformations: movelight.c
#include <GL/gl.h>
#include <GL/glu.h>
#include “glut.h”
static int spin = 0;
void init(void)
{
glClearColor (0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0);
glShadeModel (GL_SMOOTH);
glEnable(GL_LIGHTING);
glEnable(GL_LIGHT0);
glEnable(GL_DEPTH_TEST);
}
/* Here is where the light position is reset after the modeling
* transformation (glRotated) is called. This places the
* light at a new position in world coordinates. The cube
* represents the position of the light.
*/
void display(void)
{
GLfloat position[] = { 0.0, 0.0, 1.5, 1.0 };
glClear (GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT | GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT);
glPushMatrix ();
glTranslatef (0.0, 0.0, -5.0);
glPushMatrix ();
glRotated ((GLdouble) spin, 1.0, 0.0, 0.0);
glLightfv (GL_LIGHT0, GL_POSITION, position);
glTranslated (0.0, 0.0, 1.5);
glDisable (GL_LIGHTING);
glColor3f (0.0, 1.0, 1.0);
glutWireCube (0.1);
glEnable (GL_LIGHTING);
glPopMatrix ();
glutSolidTorus (0.275, 0.85, 8, 15);
glPopMatrix ();
glFlush ();
}
void reshape (int w, int h)
{
glViewport (0, 0, (GLsizei) w, (GLsizei) h);
glMatrixMode (GL_PROJECTION);
glLoadIdentity();
gluPerspective(40.0, (GLfloat) w/(GLfloat) h, 1.0, 20.0);
glMatrixMode(GL_MODELVIEW);
glLoadIdentity();
}
void mouse(int button, int state, int x, int y)
{
switch (button) {
case GLUT_LEFT_BUTTON:
if (state == GLUT_DOWN) {
spin = (spin + 30) % 360;
glutPostRedisplay();
}
break;
default:
break;
}
}
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
glutInit(&argc, argv);
glutInitDisplayMode (GLUT_SINGLE | GLUT_RGB | GLUT_DEPTH);
glutInitWindowSize (500, 500);
glutInitWindowPosition (100, 100);
glutCreateWindow (argv[0]);
init ();
glutDisplayFunc(display);
glutReshapeFunc(reshape);
glutMouseFunc(mouse);
glutMainLoop();
return 0;
}
|
GLfloat light_position() = { 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 1.0 };
glViewport(0, 0, (GLint) w, (GLint) h);
glMatrixMode(GL_PROJECTION);
glLoadIdentity();
gluPerspective(40.0, (GLfloat) w/(GLfloat) h, 1.0, 100.0);
glMatrixMode(GL_MODELVIEW);
glLoadIdentity();
glLightfv(GL_LIGHT0, GL_POSITION, light_position);
|
If the viewpoint is now moved, the light will move along with it, maintaining (0, 0, 0) distance, relative to the eye.
static GLdouble ex, ey, ez, upx, upy, upz;
void display(void)
{
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_MASK | GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_MASK);
glPushMatrix();
gluLookAt (ex, ey, ez, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, upx, upy, upz);
glutSolidTorus (0.275, 0.85, 8, 15);
glPopMatrix();
glFlush();
}
|