Energy Efficiency of LLM Inference Across Various AI Accelerators (poster)
May 8th, 2025
Categories: Applications, Software, Supercomputing, Machine Learning, Data Science, Artificial Intelligence, High Performance Computing
Authors
Brunetta, G., Lan, Z., Wu, X., Taylor, V.About
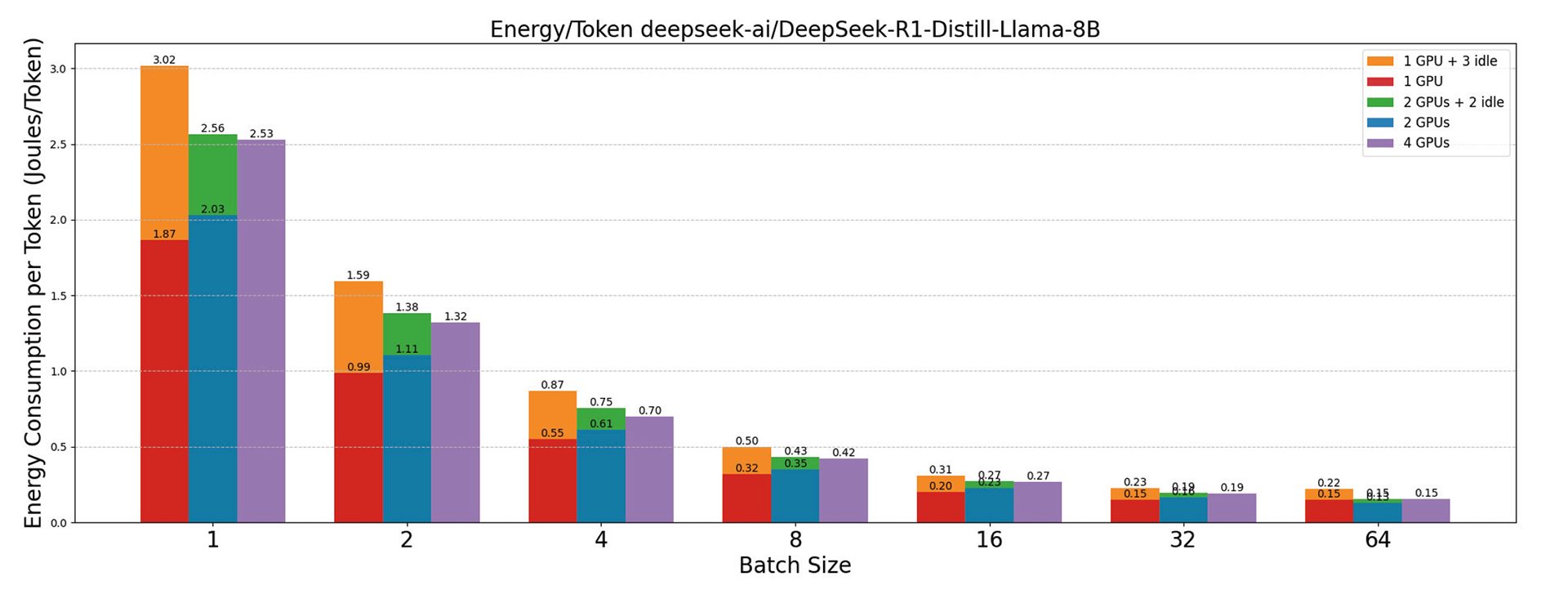
In recent years, numerous hardware accelerators have been developed to meet the rising demand for machine learning (ML) workloads, and Large Language Models inference in particular. GPUs are currently the standard for ML training and inference. However, they require substantial data movements that hurt performance and increase power consumption, making systems extremely energy-intensive. In response, many companies, including Intel, AMD, and Google, as well as numerous startups such as Groq, SambaNova, Cerebras, and Graphcore, have introduced specialized accelerators for ML workloads that leverage a dataflow design, which aims to reduce data movement and thus improve both performance and power consumption. This article presents a comparative analysis of the performance and energy efficiency of various AI accelerators and GPUs for large language model (LLM) inference, using popular open-source models evaluated on both synthetic and real-world datasets.
Resources
URL
Citation
Brunetta, G., Lan, Z., Wu, X., Taylor, V., Energy Efficiency of LLM Inference Across Various AI Accelerators (poster), The 12th Greater Chicago Area Systems Research Workshop (GCASR), Chicago, IL, May 8th, 2025. https://gcasr.org/2025/posters