Volume Encoding Gaussians: Transfer Function-Agnostic 3D Gaussians for Volume Rendering
April 20th, 2026
Categories: Supercomputing, Data Science, High Performance Computing
Authors
Dyken, L., Sewell, A., Usher, W., Debardeleben, N., Petruzza, S., Kumar, S.About
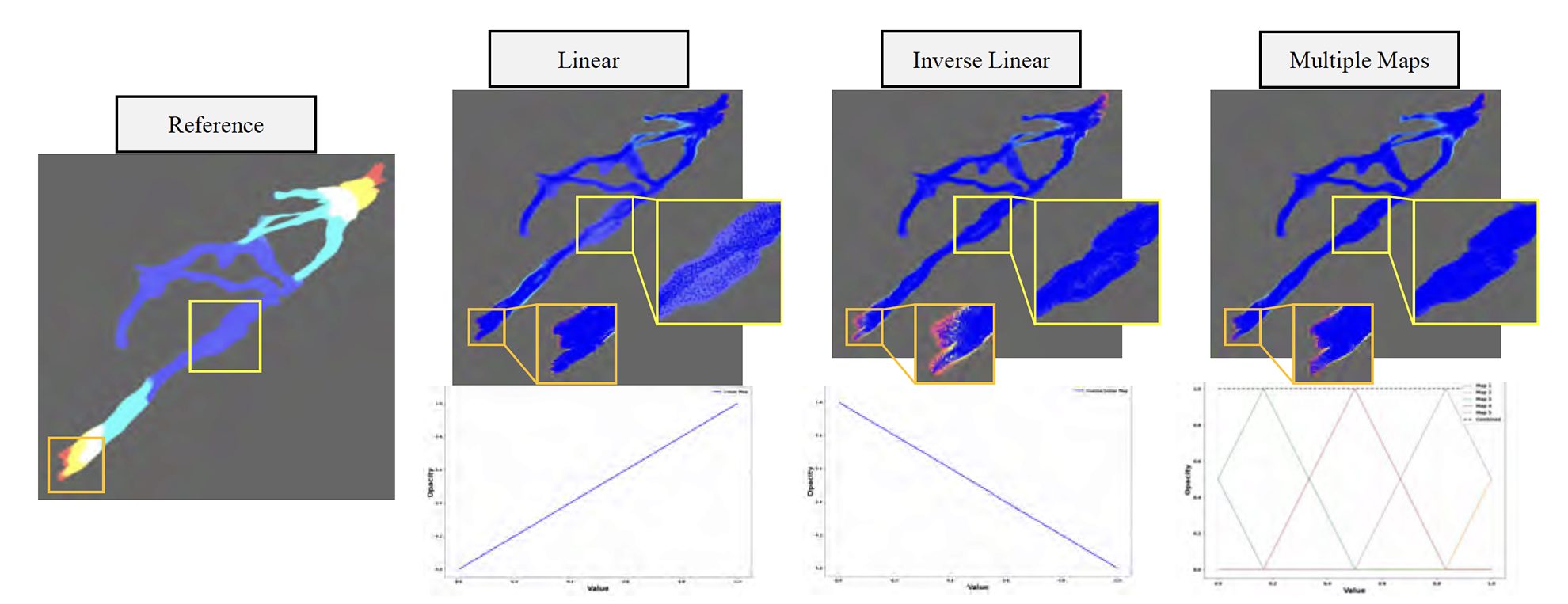
Visualizing the large-scale datasets output by HPC resources presents a difficult challenge, as the memory and compute power required become prohibitively expensive for end user systems. Novel view synthesis techniques can address this by producing a small, interactive model of the data, requiring only a set of training images to learn from. While these models allow accessible visualization of large data and complex scenes, they do not provide the interactions needed for scientific volumes, as they do not support interactive selection of transfer functions and lighting parameters. To address this, we introduce Volume Encoding Gaussians (VEG), a 3D Gaussian-based representation for volume visualization that supports arbitrary color and opacity mappings. Unlike prior 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) methods that store color and opacity for each Gaussian, VEG decouple the visual appearance from the data representation by encoding only scalar values, enabling transfer function-agnostic rendering of 3DGS models. To ensure complete scalar field coverage, we introduce an opacity-guided training strategy, using differentiable rendering with multiple transfer functions to optimize our data representation. This allows VEG to preserve fine features across a dataset’s full scalar range while remaining independent of any specific transfer function. Across a diverse set of volume datasets, we demonstrate that our method outperforms the state-of-the-art on transfer functions unseen during training, while requiring a fraction of the memory and training time.
Index Terms - Volume Rendering, 3D Gaussian Splatting
Resources
URL
Citation
Dyken, L., Sewell, A., Usher, W., Debardeleben, N., Petruzza, S., Kumar, S., Volume Encoding Gaussians: Transfer Function-Agnostic 3D Gaussians for Volume Rendering, IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics (TVCG), PacificVis 2026, Sydney, Australia, April 20th, 2026. https://www.arxiv.org/pdf/2504.13339