Head and Neck Cancer Predictive Risk Estimator to Determine Control and Therapeutic Outcomes of Radiotherapy (HNCPREDICTOR)
October 21st, 2022
Categories: Applications, Data Mining, Software, User Groups, Visualization, Visual Analytics, Deep Learning, Human Computer Interaction (HCI), Machine Learning, Data Science
Authors
van Dijk, LV, Mohamed, ASR, Ahmed, S, Nipu, N, Marai, GE, Wahid, K, Sijtsema, NM, Gunn, B, Garden, AS, Moreno, A, Hope, AJ, Langendijk, JA, Fuller, CDAbout
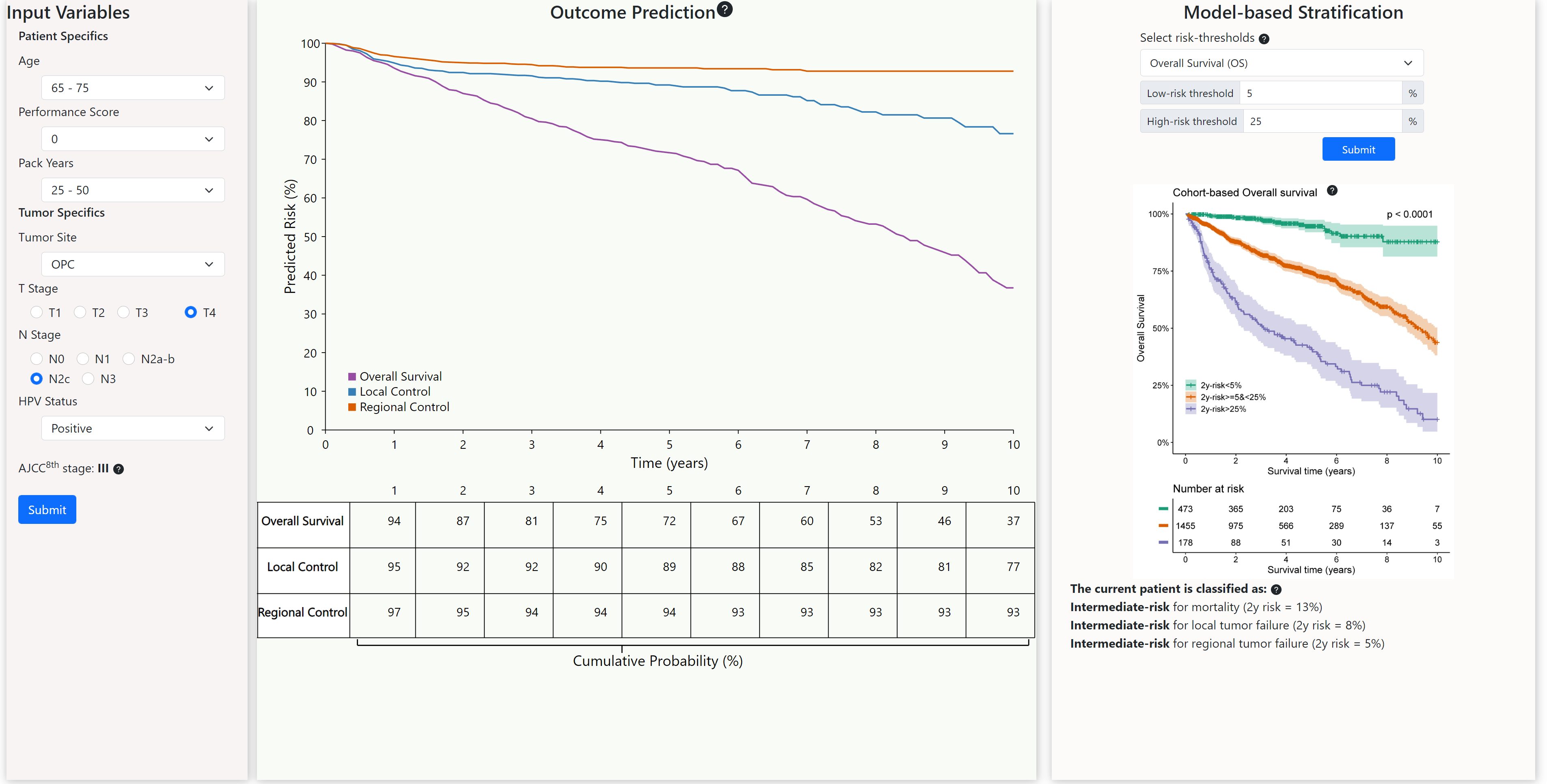
Background. Personalized radiotherapy can improve treatment outcomes of head and neck cancer (HNC) patients, where currently a ’one-dose-fits-all’ approach is the standard. The aim was to establish individualized outcome prediction based on multi-institutional international “big data” to facilitate risk-based stratification of HNC patients.
Methods. The data of 4611 HNC radiotherapy patients from three academic cancer centers was split into 4 cohorts: a training (n=2241), independent test (n=786), and external validation cohorts 1 (n=1087) and 2 (n=497). Tumor- and patient-related clinical variables were considered in a machine learning pipeline to predict overall survival (primary endpoint) and local and regional tumor control (secondary endpoints); serially, imaging features were considered for optional model improvement. Finally, patients were stratified into high, intermediate, and low risk groups.
Results. Performance score, AJCC8th stage, pack-years, and Age were identified as predictors for overall survival, demonstrating good performance in both the training cohort (c-index=0.72 [95% CI, 0.66-0.77]) and in all three validation cohorts (c-indices: 0.76 [0.69-0.83], 0.73 [0.68- 0.77], and 0.75 [0.68-0.80]). Excellent stratification of HNC patients into high, intermediate, and low mortality risk was achieved; with 5-year overall survival rates of 17-46% for the high-risk group compared to 92-98% for the low-risk group. The addition of morphological image feature further improved the performance (c-index=0.73 [0.64-0.81]). These models are integrated in a clinic-ready interactive web-interface: https://uic-evl.github.io/hnc-predictor/.
Conclusions. Robust model-based prediction was able to stratify HNC patients in distinct high, intermediate and low mortality risk groups. This can effectively be capitalized for personalized radiotherapy, e.g., for tumor radiation dose escalation/de-escalation.
See Science Direct for more information.
Resources
URL
Citation
van Dijk, LV, Mohamed, ASR, Ahmed, S, Nipu, N, Marai, GE, Wahid, K, Sijtsema, NM, Gunn, B, Garden, AS, Moreno, A, Hope, AJ, Langendijk, JA, Fuller, CD, Head and Neck Cancer Predictive Risk Estimator to Determine Control and Therapeutic Outcomes of Radiotherapy (HNCPREDICTOR), European Journal of Cancer, Elsevier, Science Direct, October 21st, 2022. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2022.10.011